Role of pancreatic enzymes
An enzyme is a type of protein that stimulates chemical reactions in the body. Digestive enzymes play a major role in the process of digestion, the breakdown of food into smaller parts that can easily be absorbed and used by the body. These enzymes are present in the digestive juices.
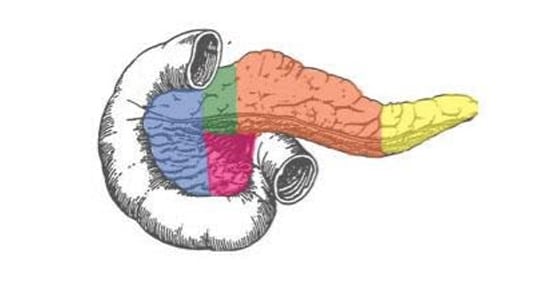
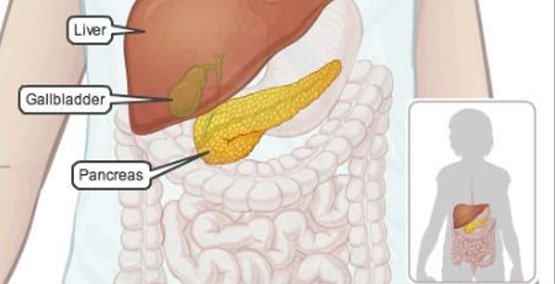
Some enzymes are made by the pancreas, a large gland near the stomach. Others enzymes are contained in bile, which is made in the liver and stored in the gallbladder. When you eat, the food stimulates release of the juices and their enzymes into the small intestine so they can digest and absorb the nutrients in food. Without these enzymes, our bodies would not be able to properly breakdown food and absorb its nutrients.
These pancreatic digestive enzymes include:
- Pancreatic Amylase: breaks down starch into sugar
- Pancreatic Lipase: breaks down fats into smaller fats and fatty acids
- Trypsin, chymotrypsin, and carboxypeptidase: breaks down proteins into amino acids
- Ribonuclease: digests RNA molecules which act as DNA messengers for controlling proteins in the body
- Deoxyribonuclease: digests DNA molecules, the carriers of genetic information in the body