Diabetes management
How to treat type 1 and type 2
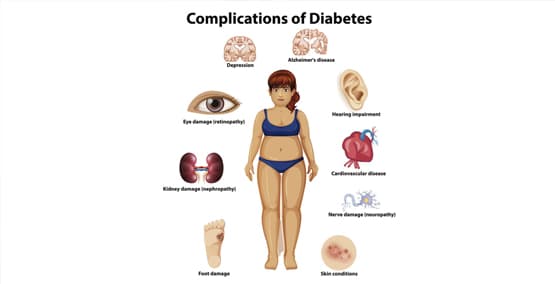
-Type 1 diabetes can only be treated with insulin injections since the pancreas is not able to make enough insulin. To keep blood sugars within normal range, most patients take 4-6 insulin injections a day or wear a pump. Type 1 diabetes is managed with insulin, diet and exercise, at this time there is no cure.

Type 2 diabetes can be treated oral or injectable medications along with diet and exercise. There are many medications that are now available to treat type 2 diabetes (DM2). The most common medication used is Metformin (Glucophage). Often times, people with DM2 will need insulin to manage their diabetes. Of particular importance in DM2 is weight management. For some people with DM2, the condition can be reversed with significant weight loss.
The Importance of Diet in Diabetes
In all types of diabetes, it is important to have a well-balanced diet. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, dairy, eggs, legumes, nuts and healthy fats is recommended. Foods that are high in sugar or that are highly processed should be limited.
People with diabetes learn how to manage the amount and type of carbohydrates they are eating. In type 1 diabetes the amount and frequency of insulin injections is designed for the amount of carbohydrates in their meal plans. In type 2 diabetes, meal plans are similar with an emphasis on controlling the amount of carbohydrates with meals and snacks. A registered dietitian nutritionist works with the patient to determine the appropriate meal plan and amount of carbohydrates at each meal and snack.
Research is underway evaluating if a low carbohydrate diet is beneficial to those with diabetes. As of now, there are no official recommendations for patients with type 1 diabetes to restrict carbohydrates. There is some evidence that lower carbohydrate diets may be helpful in managing type 2 diabetes.