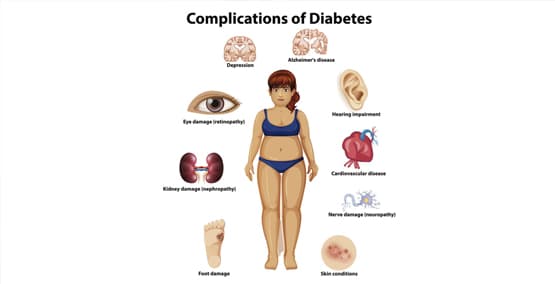
Diagnosing diabetes
4 Tests used to diagnose
-Diabetes usually is diagnosed with symptoms of increased thirst and urination. The doctor will do laboratory testing to determine if diabetes is the cause.

Laboratory Tests for Diabetes
- A fasting blood sugar test can be performed after avoiding food and drinks for at least 8 hours. A fasting blood sugar level of >125 mg/dL is suggestive of diabetes. Fasting blood sugar level above 100mg/dL is considered abnormal and would be evidence of prediabetes.
- A random blood glucose >200 mg/dL with symptoms of diabetes is suggestive of diabetes.
- An oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) can also be done to diagnose diabetes. An OGTT is done by fasting overnight followed by drinking a glucose-containing liquid in the morning. The blood glucose (BG) is measured before and 2 hours after the patient drinks the liquid. If the 2-hour blood glucose is >200 mg/dL, that is diagnostic of diabetes. If BG is between 140-199 mg/dL suggests prediabetes. If BG is <140 mg/dL is normal.
- A hemoglobin A1C is a blood test that measures what the average blood glucose level is over the past 3 months. You do not need to fast for this testing. An A1C of 6.5% or above is considered in diabetic range.
To officially diagnoses diabetes the physician may perform 2 of the above tests on different days.