Essential vitamins and minerals in pancreatic disorders
The nutrients you need in cystic fibrosis and exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
-Everyone, not just those with CF (Cystic Fibrosis) and EPI (exocrine pancreatic insufficiency), needs essential vitamins and minerals for health. In addition, everyone needs protein, carbohydrates, water and fiber. In CF and EPI, minerals, like iron , and calcium, even the others, including zinc, and magnesium are important.
People with CF and EPI need extra vitamins, especially the fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E and K because of their difficulty absorbing fat.
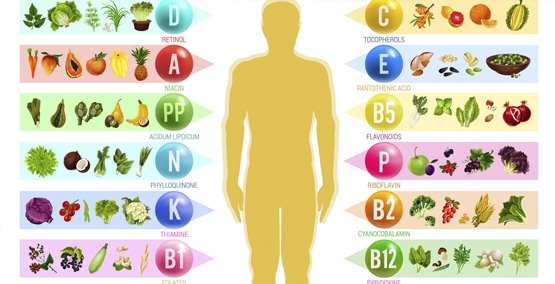
The chart below shows the essential vitamins everyone needs, their functions and where to get them. They are separated into fat soluble vitamins (require fat for absorption), water soluble vitamins (easily absorbed and excess is excreted in urine) and conditional vitamins that are only needed in certain situations.
| Water Soluble/Required | Importance | Good Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Thiamine (B1) | Carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism, nerve and muscle membranes | Grains, nuts, potatoes |
| Riboflavin (B2) | Energy use, cell respiration and repair | Dairy, meats, green vegetables, eggs, yeast |
| Pyridoxine (B6) | Enzyme activation and cofactor | Meats, vegetables, fruits, nuts, grains, legumes |
| Cyanocobalamin (B12) | Formation of genetic code, amino and fatty acid metabolism, blood cell and nerve development | Meats, eggs, milk products |
| Folate | Formation of genetic code, utilization of protein | Green vegetables, nuts, liver |
| Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) | Collagen formation/wound healing, immunity | Fruits, vegetables |
| Water Soluble/Conditional | ||
| Niacin (B3) need when prolonged diarrhea | Protein and energy utilization | Grains, poultry, fish |
| Choline Usually can be manufactured | Cell transport signaling and integrating | Milk, eggs, liver, peanuts |
| Biotin (B7) needed when tube feedings, excess egg whites | Energy metabolism activation of folate | Intestinal bacteria, organ meats, yeast, soy, nuts, cereals |
| Pantothenic acidUsually can be manufactured | Fat metabolism | Meats, whole grains, legumes, vegetables |
| Fat-Soluble Vitamins | ||
| Vitamin A | Vision, skin integrity, gene expression | Fruits, vegetables, fortified milk, fish oils |
| Vitamin D | Calcium and phosphorus absorption, role in immune regulation | Sun, Fish, eggs, fortified milk products |
| Vitamin E | Cell membrane stability, antioxidant | Fruits, vegetables, meats, oils |
| Vitamin K | Clotting | Intestinal bacteria, meats, green vegetables |
Minerals
Most people are aware they need iron to avoid anemia. The condition where the red blood cells aren't able to get oxygen to the body's cells. They also know they need calcium for their bones. These minerals are especially important in CF and EPI because anemia and low bone density are common.
Also important are magnesium and zinc when they have diarrhea. Fortunately, a short course of 2-4 weeks of supplementation will raise the levels back to normal, if the diarrhea can also be stopped.
Listed below is a table of essential minerals, functions and sources:
| Calcium | Bone formation, nerve signaling, hormone secretion | Dairy, broccoli, kale |
| Copper | Creation of bone structure, energy metabolism | Seafood |
| Chromium | Sugar metabolism | Meats, fish, grains, Brewer's yeast |
| Fluoride | Strengthening of teeth, bone formation | Fluoridated water, toothpaste, mouth rinses |
| Iron | Transportation of oxygen and energy | Meats, green vegetables, iron-fortified cereals |
| Magnesium | Bone metabolism, metabolic processes | Grains, nuts, leafy vegetables |
| Manganese | Protein and fat metabolism, bone formation | Vegetables, grains, organ meats |
| Potassium | Regulation of fluids in cells, nerve signaling, heart contractions | Fruits (bananas, oranges), vegetables |
| Selenium | Antioxidant (similar to vitamin E), part of enzyme system | Vegetables, meats, fruits, milk products |
| Sodium | Regulation of hydration and fluid in blood vessels | Salt in food preparation, processed foods |
| Zinc | Protein and fat formation, processing of genetic codes | Fish, meats |
The amount of these vitamins and minerals in the foods you eat are listed in our table on nutritional content. Some of the vitamins and minerals are listed on nutrition labels using a 2000 calorie diet as the standard. But if you need more or less than 2000 calories, your needs will be different. This USDA Tool , can calculate the amount in each food based on your individual needs.
If you don't get enough vitamins or minerals in the food that you eat, it may be helpful to take a once daily multivitamin mineral for nutritional insurance.
Of course, you always have to remember that when you eat, you have to be sure to take your PERT (pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy).